Deploying Java Spring Boot Application On Kubernetes With Db
Hands-On Guide
Deploying a Java Spring Boot Application on Kubernetes with MySQL.

WORK FLOW
lets divide the flow into small steps:
Set up the cloud server
Install the dependencies
Set up Mini-Kube
Clone the Repository
Configure the database required.
Build the project
Create the Docker images
Push the images to Dockerhub
Run the manifest files
Do port forwarding
Check JSON data to be hit on Postman
Add some data to the database using postman
Check the Database if the entries are visible
Check Mini-Kube dashboard
Source Code :
GitHub - SurendarSv/SpringBootOnK8s
Contribute to SurendarSv/SpringBootOnK8s development by creating an account on GitHub.
STEPS :
create a server t2.medium

Connect through SSH:
Update the packages and package caches. Use commands :
#sudo su
#yum update -y
Install docker. Use commands :
#yum install docker
#systemctl enable docker
#systemctl start docker
#systemctl status docker
#docker — version
Check Docker version

Start docker and check status docker

Conntrack : is a short for Connection Tracking, is a crucial component in Kubernetes networking that is required for reliable communication between containers and services. It is responsible for tracking network connections and their states, allowing the Kubernetes networking stack to function properly.
Conntrack is needed for minikube.
Install Conntrack
#yum install conntrack -y
Install git. Use command :
#yum install git
#git --version
To download the latest version of Minikube for the Linux platform.
#curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-linux-amd64
#ls -lrta
minikube has been downloaded.

Install minikube. Use command :
#sudo install minikube-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/minikube
Start minikube:
minikube is platform which gives k8s
#/usr/local/bin/minikube start --force --driver=docker
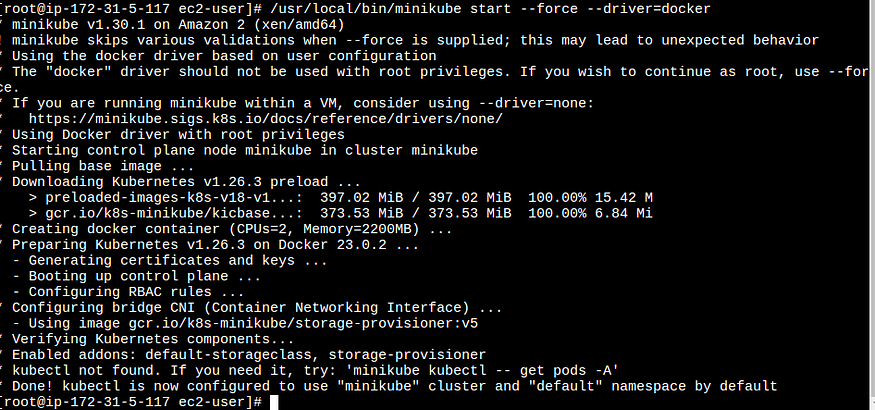
Why do we need docker driver?
Kubernetes is a platform which is running on docker. Docker is helping Kubernetes to run.

Check minikube version
#/usr/local/bin/minikube version

Install kubectl:
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"
Giving permissions to kubectl
sudo install -o root -g root -m 0755 kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
Check version
/usr/local/bin/kubectl version

Install git
Clone the repo:
yum install git -y
git --version
cd /opt
git clone https://github.com/SurendarSv/SpringBootOnK8s.git

DB installation / make the DB up:
/usr/local/bin/kubectl get pods
/usr/local/bin/kubectl create -f db-deployment.yaml
To create the persistent database and other services.


we have change dir to /usr/local/bin
Because minikube has been installed there.
cd /usr/local/bin

Check pods:
kubectl get pods
Check database i.e going inside the container
/usr/local/bin/kubectl exec -it <POD_NAME>/bin/bash
IN MY CASE
/usr/local/bin/kubectl exec -it mysql-f759455cd-n5gw6 /bin/bash
Enter the DB,password is : root
mysql -u root -p

DB created from the deployment file.DB name : singamlabs

now exit the pod.
Install maven now and check version:
yum install maven -y
mvn -v

No images are available.
docker images
Create the docker image now.
docker build -t surendar24/springboot-crud-k8s:1.0 .

Login to docker hub:
docker login

Push the image to docker hub:
docker image push surendar24/springboot-crud-k8s:1.0 .

IMAGE is pushed to docker hub:

execute the app. deploy.yaml file.
/usr/local/bin/kubectl apply -f app-deployment.yaml
Check pods
/usr/local/bin/kubectl get pods
4 pods -> 3 are replicas
Check svc available.
/usr/local/bin/kubectl get svc

minikube ip
/usr/local/bin/minikube ip

Why multiple pods/pod replicas?
Replicas are being created so that the traffic will get distributed.
PORT-FORWARDING
Port forwarding is a networking technique used to redirect network traffic from one port on a host to another port on a different host or the same host. In the context of Kubernetes, port forwarding allows you to access services running inside a Kubernetes cluster from your local machine or another remote host.
Put port forward.
/usr/local/bin/kubectl port-forward --address 0.0.0.0 svc/springboot-crud-svc 8080:8080 &
Update it.

Now go back to postman again. And add a entry.
POST method :

GET method :

/usr/local/bin/kubectl exec -it mysql-f759455cd-n5gw6 /bin/bash

The Changes can be observed instanly.


Exit mySQL
Open the Dashboard of K8S.
Open a new terminal of your server and then perform this command.
Inside EC2 our minikube is running so we are setting a proxy for all the local address.
/usr/local/bin/kubectl proxy --address='0.0.0.0' --accept-hosts='^*$'
The proxy server is started on port 8001.
Open another terminal:
/usr/local/bin/minikube dashboard

change the IP address with your EC2 server IP address and port 8081.
In my case:
http://20.234.84.191:8001/api/v1/namespaces/kubernetes-dashboard/services/http:kubernetes-dashboard:/proxy/


Hence Deployment a Java Spring Boot Application on Kubernetes with MySQL.
Detailed Project OverView:
youtube.com/watch?v=tfoOBn_hcgc&list=PL..
Credits: Praveen Singampalli
Thanks for reading :)